Access Control
The administrator can limit devices or protocols that can be connected to the machine to avoid unintended access.
Also, the administrator can select a security level at which to enable or disable a protocol and to configure the port status.
Limiting machine access (access control)
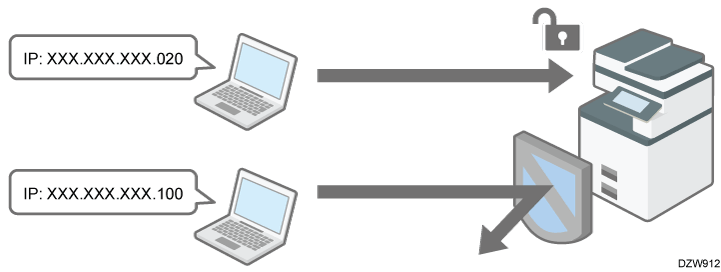
You can limit the IP addresses from which devices can access the machine or limit machine access with a firewall.
For example, when specifying the range of IP address from "192.168.15.1" to "192.168.15.99", the machine cannot be accessed from IP addresses in the range from 192.168.15.100 to 255.
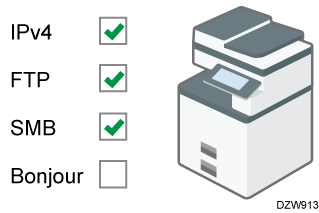
Disabling unused protocols
The protocol setting can be changed on the control panel, in Web Image Monitor, or by using other setting methods. The protocols that can be configured vary depending on the method. Confirm the protocol to configure in Protocol Setting Method List and follow the instruction.
Limiting the IP addresses from which devices can access the machine
Specify the range of the IP address that can access the machine.
You can limit access from the following protocols.
LPR, RCP/RSH, FTP, Bonjour, WSD (Device), WSD (Printer), IPP, DIPRINT, SNMP, telnet, NBT
The machine also limits access from Web Image Monitor.
Log in to the machine as the network administrator from Web Image Monitor.
Logging in to the Machine as an AdministratorClick [Configuration] on the [Device Management] menu.
Click [Access Control] in the "Security" category.
In "Access Control Range", click [Active] and specify the range of IP addresses that have access to the machine.
- To specify an IPv4 address, enter a range that has access to the machine in [Access Control Range].
- To specify an IPv6 address, select [Range] or [Mask] in "Access Control Range", and then enter a range that has access to the machine.
- To allow guest users to print directly via Wi-Fi using smart devices, select [Active] for "Access Control for Direct Connection (Group Owner Mode Only)".
Click [OK].
Log out of the machine, and then exit the Web browser.
Limiting machine access with a firewall
You can block machine access and then allow access only from/to the IP addresses specified in reception/transmission filters. Specify sets of an IP address, a port number, and a protocol as filters. You can configure up to five filters each for reception and transmission.
Log in to the machine as the network administrator from Web Image Monitor.
Logging in to the Machine as an AdministratorClick [Configuration] on the [Device Management] menu.
Click [Access Control] in the "Security" category.
In Access Control Range, click [Active (Firewall)] and specify reception and transmission filters.
Specify the following for each reception/transmission filter.
IPv4/IPv6 reception filter
Remote IP Address: Enter source IP addresses from which to allow incoming communications. To allow incoming communications from all IP addresses, select [All].
Local Port Number: Enter a port number on the machine through which to allow incoming communications. To allow incoming communications to all ports, select [All].
Protocol: Select a protocol in which to allow communications.
IPv4/IPv6 transmission filter
Remote IP Address: Enter destination IP addresses to which to allow outgoing communications. To allow outgoing access to all IP addresses, select [All].
Remote Port Number: Enter port numbers to which to allow outgoing communications. To allow outgoing communications to all ports, select [All].
Protocol: Select a protocol in which to allow communications.
Click [OK].
Log out of the machine, and then exit the Web browser.
When filters are not configured properly, access to the machine is not possible. In such a case, specify [Inactive] for [System Settings]
[Settings for Administrator]
[Security]
[Access Control Function] on the control panel.
You can view the protocol setting methods in the following list:
1: Control Panel 2: Web Image Monitor 3: telnet 4: Device Manager NX 5: Remote Communication Gate S
Protocol/Port |
Setting method |
Function that cannot be used when Protocol/Port is disabled |
|---|---|---|
IPv4 - |
1, 2, 3 |
All applications that operate over IPv4 (IPv4 cannot be disabled from Web Image Monitor when using IPv4 transmission.) |
IPv6 - |
1, 2, 3 |
All applications that operate over IPv6 |
IPsec - |
1, 2, 3 |
Encrypted transmission using IPsec |
FTP TCP:21 |
2, 3, 4, 5 |
Transmissions that require FTP (You can restrict only the personal information from being displayed by settings on the control panel.) |
telnet TCP:23 |
2, 4 |
Transmissions that require telnet |
SMTP TCP:25 (variable) |
1, 2, 4, 5 |
E-mail notification function that requires SMTP reception |
HTTP TCP:80 |
2, 3 |
Transmissions that require HTTP Print using IPP on port 80 |
HTTPS TCP:443 |
2, 3 |
Transmissions that require HTTP (You can make settings to require SSL transmission only and to reject non-SSL transmission using the control panel or Web Image Monitor.) |
NBT UDP:137/UDP:138 |
3 |
NetBIOS designated functions on the WINS server |
SNMPv1-v2 UDP:161 |
2, 3, 4, 5 |
Transmissions that require SNMPv1/v2 (Using the control panel, Web Image Monitor, or telnet, you can specify SNMPv1/v2 to prohibit configuration and make it read-only.) |
SNMPv3 UDP:161 |
2, 3, 4, 5 |
Transmissions that require SNMPv3 (You can make settings to require SNMPv3 encrypted transmission only and to reject non-SNMPv3 encrypted transmission using the control panel, Web Image Monitor, or telnet.) |
RSH/RCP TCP:514 |
2, 3, 4, 5 |
Transmissions that require RSH Network TWAIN (You can prohibit only personal information from being displayed by the settings on the control panel.) |
LPR TCP:515 |
2, 3, 4, 5 |
Transmissions that require LPR (You can restrict only personal information from being displayed by the settings on the control panel.) |
IPP TCP:631 |
2, 3, 4, 5 |
Transmissions that require IPP |
IP-Fax TCP:1720 (H.323) UDP:1719 (Gatekeeper) TCP/UDP:5060 (SIP) TCP:5000 (H.245) UPD:5004, 5005 (Voice) TCP/UDP:49152 (T.38) |
1, 2, 4, 5 |
IP-Fax using H.323, SIP, or T.38 |
Bonjour UDP:5353 |
2, 3 |
Transmissions that require Bonjour |
@Remote TCP:7443 TCP:7444 |
1, 2, 3 |
RICOH @Remote |
DIPRINT TCP:9100 |
2, 3, 4, 5 |
Transmissions that require DIPRINT |
RFU TCP:10021 |
1, 2, 3 |
Remote updating of firmware |
WSD (Device) TCP:53000 (variable) |
1, 2, 3 |
Transmissions that require WSD (Device)
|
WSD (Printer) TCP:53001 (variable) |
1, 2, 3 |
Transmissions that require WSD (Printer) |
LLMNR UDP:5355 |
2, 3 |
Name resolution requests using LLMNR |

For details about the telnet command, see "Device Monitoring (TELNET)" on our website.
For details about the settings in Device Manager NX or Remote Communication Gate S, see the user's manual of each tool.
Log in to the machine as the machine administrator on the control panel.
Logging in to the Machine as an Administrator
When custom-privileges administrators are registered, you can log in to the machine as a custom-privileges administrator with the Network/Interface privilege as well.
Logging in to the Machine as a Custom-Privileges AdministratorOn the Home screen, press [Settings].

Press [System Settings].
Press [Network/Interface]
 [Effective Protocol].
[Effective Protocol].From the list next to each unused protocol, select [Inactive].
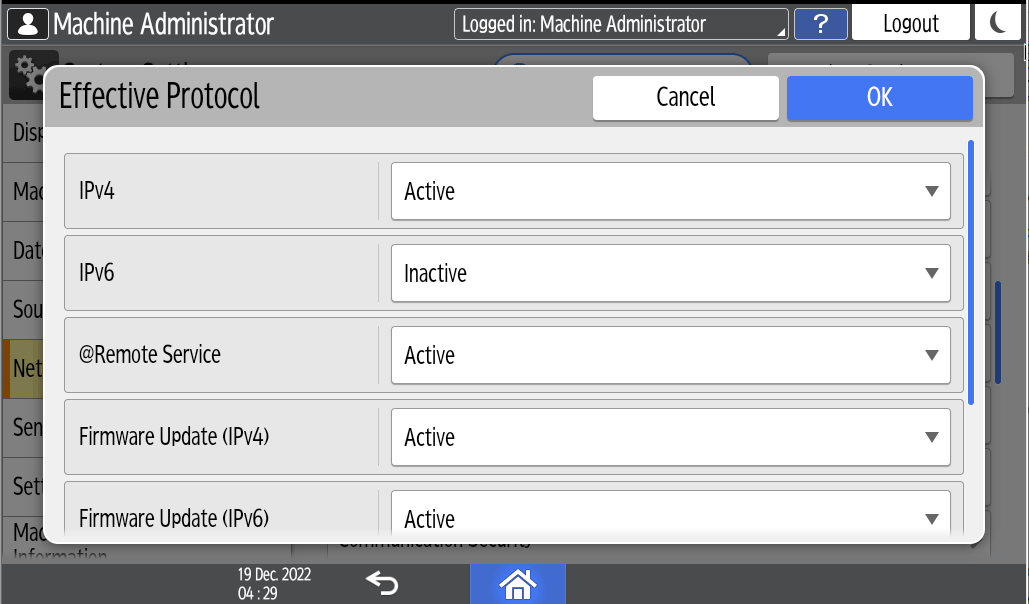
Press [OK].
Press [Home] (
 ), and then log out of the machine.
), and then log out of the machine.
Log in to the machine as the network administrator from Web Image Monitor.
Logging in to the Machine as an Administrator
When custom-privileges administrators are registered, you can log in to the machine as a custom-privileges administrator with the Security privilege as well.
Logging in to the Machine as a Custom-Privileges AdministratorClick [Configuration] on the [Device Management] menu.
Click [Network Security] in the "Security" category.
Specify protocols to disable or port numbers to close.
Click [OK].
Log out of the machine, and then exit the Web browser.